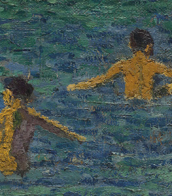what school did he go to

Francis Harry Compton Crick was a British molecular biologist, biophysicist and neuroscientist. He won the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1962.
During World War II he had to work on developments for the military, and in 1947 he turned to biology at the Strangeways Research Laboratory, University of Cambridge. In 1949 he moved to the University Medical Research Council at Cavendish Laboratories. Using X-ray diffraction studies of DNA by biophysicist Maurice Wilkins (1916-2004) and X-ray diffraction images taken by Rosalind Franklin, biophysicist James Watson and Crick were able to construct a molecular model consistent with the known physical and chemical properties of DNA.
This achievement became a cornerstone of genetics and was regarded as one of the most important discoveries of 20th century biology. In 1962, Francis Crick, along with James Watson and Maurice Wilkins, won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for determining the molecular structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the chemical ultimately responsible for the hereditary control of life functions.
From 1977 until the end of his life, Crick served as professor emeritus at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies in San Diego, California, where he conducted research on the neurological basis of consciousness. He also wrote several books. In 1991, Francis Crick received the Order of Merit.


Paul Gauguin, a French artist born in Paris in 1848, is renowned for his significant contributions to Post-Impressionism, Primitivism, and Synthetism. Gauguin's art is distinguished by his experimental use of color and style, which set him apart from the traditional Impressionist movement.
Gauguin's early life was marked by a period in Peru, which influenced his artistic perspective. Initially, he pursued a career in stockbroking but soon turned to art, driven by financial necessity and a growing passion. His artistic journey began under the mentorship of Impressionist artist Camille Pissarro and through exposure to the works of other avant-garde artists.
The hallmark of Gauguin's work is his exploration of non-Western cultures, particularly during his time in Tahiti and the Marquesas Islands. This period saw the creation of some of his most famous works, including "Where Do We Come From? What Are We? Where Are We Going?" His paintings from this era, characterized by vivid colors and Symbolist themes, reflect a fusion of cultural influences and his quest for a "primitive" expression of spiritual and emotional states.
Despite his innovative style, Gauguin struggled with financial difficulties and health issues throughout his life. His work received little recognition during his lifetime, but posthumously, he gained acclaim for influencing modern artists like Pablo Picasso and Henri Matisse.
Today, Gauguin's works are celebrated in galleries and museums worldwide for their unique blend of cultural influences and artistic innovation. His enduring legacy is a testament to his unique vision and the profound impact he had on the art world.
Collectors and experts in art and antiques, stay updated on new product sales and auction events related to Paul Gauguin. Sign up now for exclusive updates and immerse yourself in the world of this visionary artist.


Jack W. Aeby is an American environmental physicist and photographer.
Aeby attended the University of Nebraska and was one of the first civilian employees of the Manhattan Project beginning in 1942. He worked on the project in many areas, starting with human transportation, then he was assigned as the chemical warehouse superintendent.
On July 16, 1945, while at base camp with all the official photographic equipment, Aeby took the only well-exposed color photograph of the first detonation of a nuclear weapon at the Trinity Nuclear Test Site in New Mexico, for which he became famous. The rest of the film was destroyed by the explosion. At the time of the photograph, Aeby was a civilian working in the health physics group with Emilio Segre.
Jack Aeby continued to work at Los Alamos during the Crossroads tests and eventually witnessed nearly 100 nuclear explosions. He then returned to work at Los Alamos National Laboratory in the Department of Health Physics.









![Thomas Pennant | The British zoology. London, [1761]-1766, fine coloured plates](/assets/image/picture_3553052/cf9ca/5vmcpiiefschwxfd644hmmxujwr-inwgmjwdqtkchu1wuxzb45ec2hhjerbwp1699094282jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![Thomas Pennant | The British zoology. London, [1761]-1766, fine coloured plates](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_3553052/cf9ca/5vmcpiiefschwxfd644hmmxujwr-inwgmjwdqtkchu1wuxzb45ec2hhjerbwp1699094282jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)